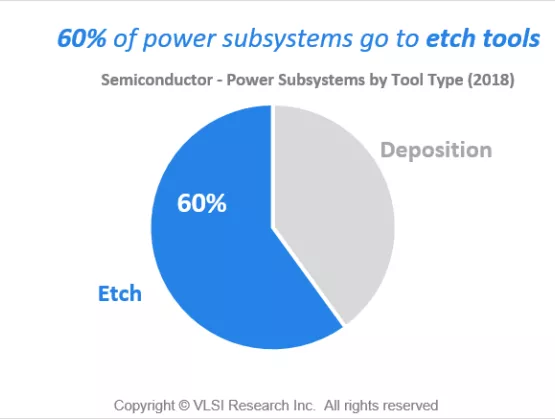
Process power and reactive gas subsystems for semiconductor manufacturing equipment have grown at a CAGR of 21% since 2013. The segment growth is considerably above the critical subsystems industry average of 9.5% and is attributable to higher demand for vacuum processing equipment over the period.
Process power and reactive gas subsystems now account for approximately 12% of all expenditures on critical subsystems used on semiconductor manufacturing equipment, up from 7% in 2013. The main driver of this exceptional growth has been the rise in vacuum processing steps (deposition and etch) during the manufacturing processes of both logic and memory devices. Most deposition and etch processes require an RF generator to provide a plasma energy source in the chamber, increasing demand for tools with power subsystems such as RF power supplies and matching networks.
Multiple patterning and the advent of 3D NAND in high-volume manufacturing have significantly increased the number of deposition and etch processing steps and, in the case of 3D NAND, longer and more difficult etch processes are requiring a wider range of power solutions. Further analysis shows that 3D NAND has been the principle growth catalyst, with the total share of power subsystems going to memory applications increasing 8 percentage points since 2013. Memory applications now account for almost half of all power subsystems demand in 2018.
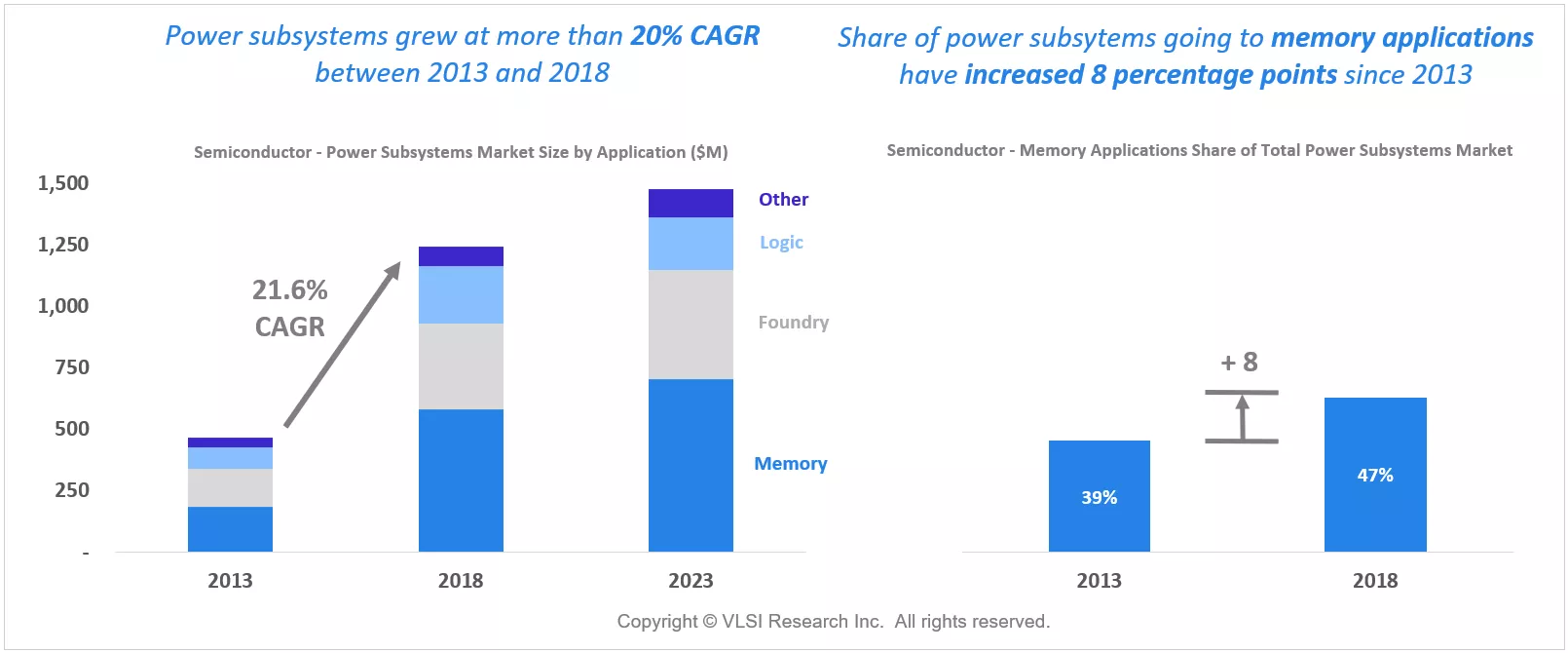
Interestingly, investigation of power subsystems by tool type reveals that a clear majority of power subsystems (60%) find their way on to etch tools with only 40% on deposition tools. This can be explained by the fact that more delicate etch processes can require multiple RF power solutions per tool, whereas deposition does always use plasma energy sources, for example in thermal deposition processes.
Despite the staggering growth performance of the power subsystems segment over the past five years, we expect the growth rate to moderate significantly in the run-up to 2023. Now that 3D NAND has been adopted in high-volume manufacturing, we expect the rate of increase in vacuum/plasma processing steps to slow down. The introduction of EUV also has the potential to taper demand for vacuum processing equipment. However, it is not expected the reverse the trend as multiple patterning techniques will still be needed in conjunction with EUV to achieve the desired improvements in device density and performance. The future growth trend for power and reactive gas subsystems is forecast to be in line with the critical subsystems industry average at approximately 2.0% CAGR until 2023.
For more information about Critical Subsystems and VLSI Research, please visit www.vlsiresearch.com/public/csubs
Julian West is a technical and market analyst at VLSI Research Europe.